What Is the Role of Mud Pump in Horizontal Directional Drilling Field?
In Horizontal Directional Drilling construction (such as horizontal directional drilling pipe jacking method, micro tunnel construction, etc.), the mud pump is one of the core supporting equipment, and its function revolves around “ensuring the safety, efficiency, and accuracy of underground tunnel or pipe construction”.
It can be specifically divided into the following five core functions, and each function is deeply bound to the core requirement of Horizontal Directional Drilling “not excavating the surface and protecting the surrounding environment”:
Core function one: slag removal and hole cleaning to prevent blockage of the holes
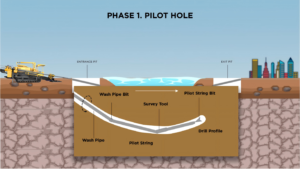
Horizontal directional drilling requires drilling pilot holes or expanding holes underground first, which will produce a large amount of impurities such as rock debris, slag, sand particles, etc. If impurities accumulate in the hole, it can cause the drill rod to become stuck, the drill bit to wear more severely, and even lead to the collapse of the borehole.

The function of the mud pump is to transport the prepared “mud” (water+bentonite+additives) to the bottom of the borehole through high pressure. The mud will wrap around the rock debris to form a “mud residue mixture”, and then the mixture will be discharged from the hole in the opposite direction to the mud treatment system on the ground (such as sedimentation tank, separator) through the circulating power of the mud pump, achieving “drilling while cleaning” and ensuring the smoothness of the borehole.
Core Function two: Stable Wall Protection to Prevent Hole Collapse
No dig drilling construction of boreholes is often located in underground soil (such as soft soil, sand layers) or rock formations. If the borehole wall lacks support, it is prone to collapse due to soil self weight and groundwater pressure (especially for horizontal or large-diameter boreholes). Once collapsed, it may cause drill pipe breakage, ground settlement, and even damage to underground pipelines (such as water pipes and cables).
The mud transported by the mud pump will form a dense “mud film” on the surface of the hole wall (usually 1-5mm thick), which can isolate the erosion of water on the hole wall. At the same time, it uses the “static hydraulic pressure” of the mud itself to balance the soil pressure and water pressure outside the hole, which is equivalent to building a “temporary support layer” for the hole wall, firmly fixing the structure of the hole wall and avoiding the risk of collapse.

Core Function Three: Cooling and Lubrication, Protecting Construction Equipment
When Horizontal Directional Drilling drilling equipment (such as drill bits, drill rods) operate at high speeds underground (speeds can reach tens to hundreds of revolutions per minute), the friction between the drill bit and rock/soil generates a large amount of heat, and the friction between the drill rod and the hole wall can cause mechanical wear – if the temperature is too high, it may cause the alloy cutting edge of the drill bit to soften and the drill rod to deform; If the wear is severe, it will shorten the service life of the equipment and even cause equipment failure.
The mud transported by the mud pump can directly contact the drill bit and drill rod: on the one hand, the flow of mud will take away the heat generated by friction, controlling the equipment temperature within a safe range (usually ≤ 60 ℃); On the other hand, the bentonite component in the mud has good lubricity, which can form a “lubricating film” between the drill rod and the hole wall, and between the drill bit and the rock debris, reducing mechanical friction and equipment wear.
Core Function Four: Auxiliary Guidance, Improving Construction Accuracy
No dig drilling construction (such as horizontal directional drilling crossing highways and rivers) requires extremely high “drilling trajectory accuracy” (deviation needs to be controlled within a few centimeters), and requires real-time monitoring of drilling direction and adjustment of drill bit angle through “measurement while drilling (MWD) equipment”.
MWD equipment is usually installed in the drill rod behind the drill bit, and the signals it emits (such as electromagnetic signals and acoustic signals) need to be transmitted to the ground receiving system through “mud” as a transmission medium – the mud pumped by the mud pump forms a continuous “fluid channel” in the hole, and the signals can be quickly transmitted through the mud. If the mud supply is interrupted or the pressure is unstable, it will cause signal attenuation and increase measurement errors. Therefore, the stable operation of the mud pump is a key auxiliary condition to ensure smooth transmission of guiding signals and improve trajectory accuracy.
Function extension: Adapt to different processes and adjust mud parameters
Different Horizontal Directional Drilling techniques (such as horizontal directional drilling, mud water balance pipe jacking, micro tunnels) have different performance requirements for mud such as viscosity, specific gravity, and water loss. Mud pumps can accurately control the flow rate, pressure, and coverage range of mud in the hole by adjusting the “displacement” (unit time delivery rate, usually 50-500 m ³/h) and “pressure” (usually 1-20MPa):
-Soft soil formation: It is necessary to reduce the mud flow velocity to avoid scouring the hole wall;
-Sand layer: Need to increase mud viscosity and enhance slag carrying capacity;
-Top pipe construction: It is necessary to inject “lubricating mud” into the outer wall of the pipe section through a mud pump to reduce the frictional resistance between the pipe section and the soil, and to lower the difficulty of jacking.
Summary: The “Irreplaceability” of Mud Pumps in No Dig Drilling
The core challenge of Horizontal Directional Drilling construction is the invisibility and complexity of underground operations. Mud pumps, through their four core functions of “slag discharge, wall protection, cooling, and guidance,” directly solve key problems such as tunnel blockage, collapse, equipment damage, and insufficient accuracy. They are the core link connecting “ground equipment” and “underground construction”, and their performance (such as pressure stability and displacement adjustment range) directly determines the efficiency, safety, and construction quality of Horizontal Directional Drilling engineering.
- Core function one: slag removal and hole cleaning to prevent blockage of the holes
- Core Function two: Stable Wall Protection to Prevent Hole Collapse
- Core Function Three: Cooling and Lubrication, Protecting Construction Equipment
- Core Function Four: Auxiliary Guidance, Improving Construction Accuracy
- Function extension: Adapt to different processes and adjust mud parameters
- Summary: The "Irreplaceability" of Mud Pumps in No Dig Drilling
SHARE:
More Posts for You
- How Does Horizontal Directional Drilling Work?
- Don’t Underestimate a Can of Grease: It’s the “Lifeline” of Your HDD Drill Pipe
- What Should I Pay Attention to When Using Mud Motors in HDD Drilling?
- Why Are Friction Welded Drill Pipes Favored by More and More Customers?
- How to Choose the Right Drill Rod for Your Horizontal Directional Drilling Project?
- From Overwhelmed to Confident: How to Choose a Pump That Actually Works for You
- Why the Right Rod Isn’t Just “Any Rod” for Your Ditch Witch JT30
- HDD Drill Rods for Vermeer 24×40